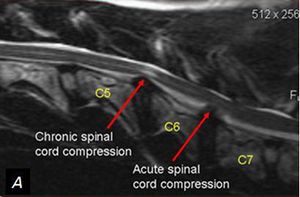
A positive Hoffman's reflex may indicate an upper motor neuron lesion or a pyramidal sign Hoffmann's reflex may be seen in the following conditions Multiple sclerosis ALS Diseases which cause spinal cord compression (myelopathy) such as cervical spondylitis, tumors, or degenerative arthritisPatient with cervical myelopathy demonstrating Hoffman's and inverted brachioradialis reflex Cord compression seen as evidenced by effacement of cerebrospin During a standard neurological exam, the Hoffman sign is common, and a positive sign can aid in the diagnosis However, a 18 systematic review, with level 1 evidence, on the utility of the Hoffman sign for the diagnosis of degenerative cervical myelopathy found insufficient data to support the use of the exam alone to confirm or refute a diagnosis of degenerative

Cervical Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Wayne Cheng Md Instructor
Hoffman sign myelopathy
Hoffman sign myelopathy-Cervical myelopathy is a common degenerative condition caused by compression on the spinal is now difficult to open jars and use her keys On physical exam she is unable to perform a tandem gait, has positive Hoffman's signs bilaterally, and has 3 but she has significant bilateral intrinsic hand weakness and a positive Hoffmann's sign(the Lhermitte sign) Bladder and/or bowel incontinence and quadriparesis usually signif y late stage myelopathy and develop because of long tract involvement, resulting in reduced sphincter control, and affect between 15% to 50% of patients 7,22 It is



S9ab564d99fcaaf1d Jimcontent Com
Hoffman's sign can be a feature of myelopathy involving the cervical spinal cord It is a test performed by doctors during their neurological examination By holding a patient's hand so that it is weightless, and flicking the nail of their middle finger, a positive test (ie one suggesting central nervous disease) causes a reflex to make their thumb and index finger contract spontaneously The Hoffman sign has a prevalence of 2% in the general population, although a positive predictive value of 68% and negative predictive value of 70% for CSM make it a useful adjunct in diagnosis 33,34 Sensory changes due to compression of the spinothalamic tract, posterior column, and spinal roots can lead to changes in pain, temperature, proprioception, andPositive myelopathy signs (Hoffman's sign, finger escape and ten second test) These patients showed moderate to severe stenosis z C5/6 on MR imaging The remaining four (6%) patients in Group 1 did not demonstrate any Wazir sign apart from the absence of Hoffman's sign and ten second test in two patients and finger escape
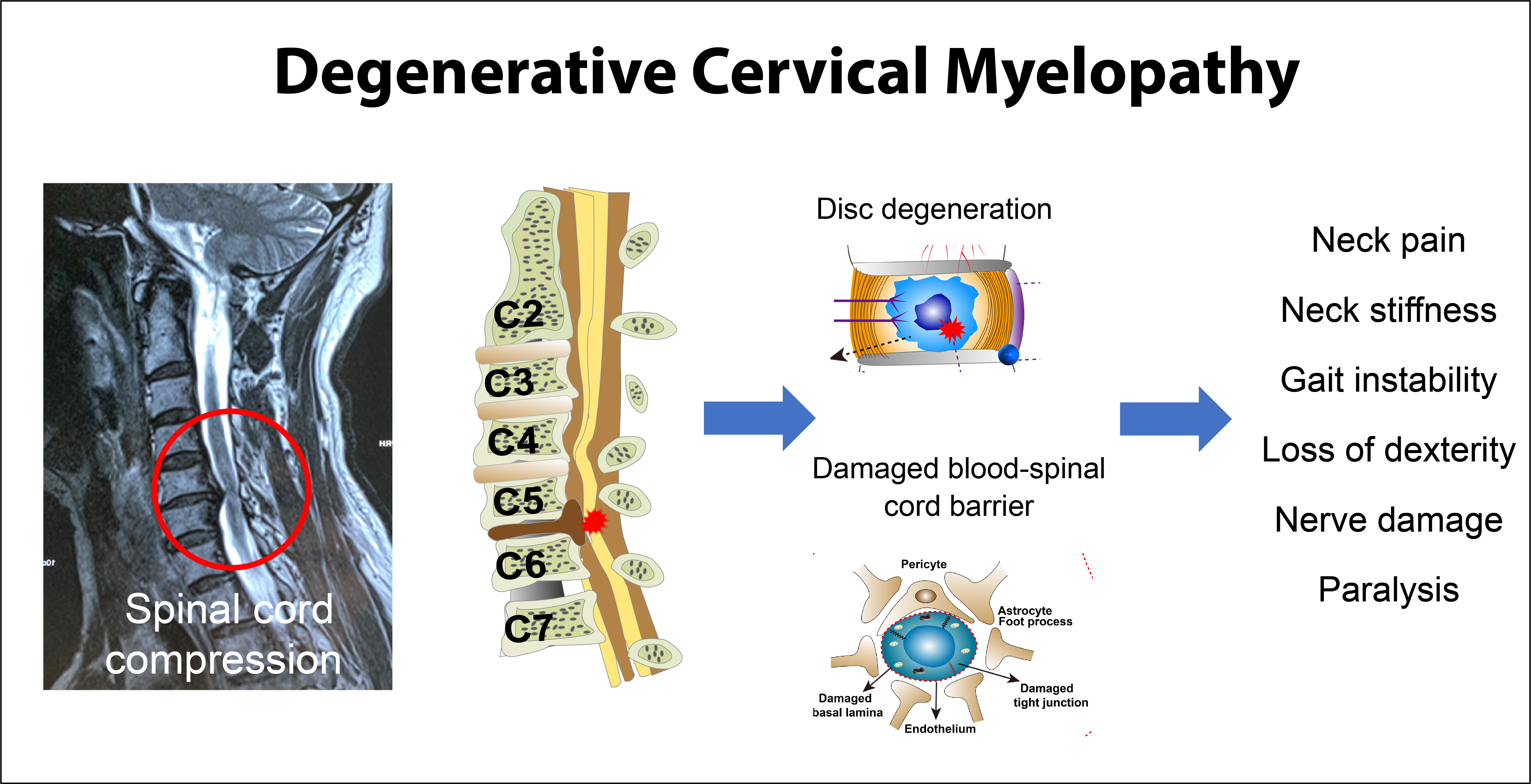
Therefore, the dynamic Hoffman's sign may prove of use in diagnosing early cervical spondylitic myelopathy Sometimes patients with true cervical myelopathy don't have a positive Hoffman's sign Although less reliable early on, when the Babinski test is positive, there is almost always a real neurologic problem Other objective neurologicalCompared with the Babiniski sign, the Hoffman sign is more prevalent in patients surgically treated for cervical myelopathy and is more likely to be found in patients with less severe neurologicalMyelopathy is an injury to the spinal cord due to severe compression that may result from trauma, congenital stenosis, degenerative disease or disc herniation The spinal cord is a group of nerves housed inside the spine that runs almost its entire length When any portion of the spinal cord becomes compressed or constricted, the resulting
Hoffman's Sign How You Get and What It Means He Hoffman sign Is an abnormal reflex response consisting of flexing the fingers of the hand by pressing the middle finger nail Although it is generally associated with pathologies such as pyramidal syndrome, it can occur in healthy people who have exalted reflexes (which is called hyperreflexia) Cervical myelopathy is a condition describing a compression of the spinal cord at the cervical level of the spinal column resulting in spasticity (sustained muscle contractions), Hoffman sign Examiner will extend the distal phalanx of the long finger Articles included were published in English or French language, rated as QUADAS level 3 or higher with a minimum 10 patients presenting with cervical complaints having undergone the Hoffman sign Excluded studies recruited patients with a nondegenerative type of cervical myelopathy, and/or no evaluation with magnetic resonance imaging Results




Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy The College Of Family Physicians Of Canada




Cervical Radiculopathy Vs Myelopathy
Object The Hoffmann sign is commonly used in clinical practice to assess cervical spine disease It is unknown whether the sign correlates with the severity of myelopathy, and no consensus exists regarding the significance of a positive sign in asymptomatic individualsHoffmann's reflex (Hoffmann's sign, sometimes simply "Hoffmann's", also finger flexor reflex) is a neurological examination finding elicited by a reflex test which can help verify the presence or absence of issues arising from the corticospinal tractIt is named after neurologist Johann Hoffmann Usually considered a pathological reflex in a clinical setting, the Hoffmann's reflex hasClonus, Babinski, inverted radial reflex, Hoffman sign Search for Similar Articles You may search for similar articles that contain these same keywords or you may modify the keyword list to augment your search




Common Cervical Spine Disorders Diagnosis And Treatment Wayne



Cervical Myelopathy Vs Radiculopathy
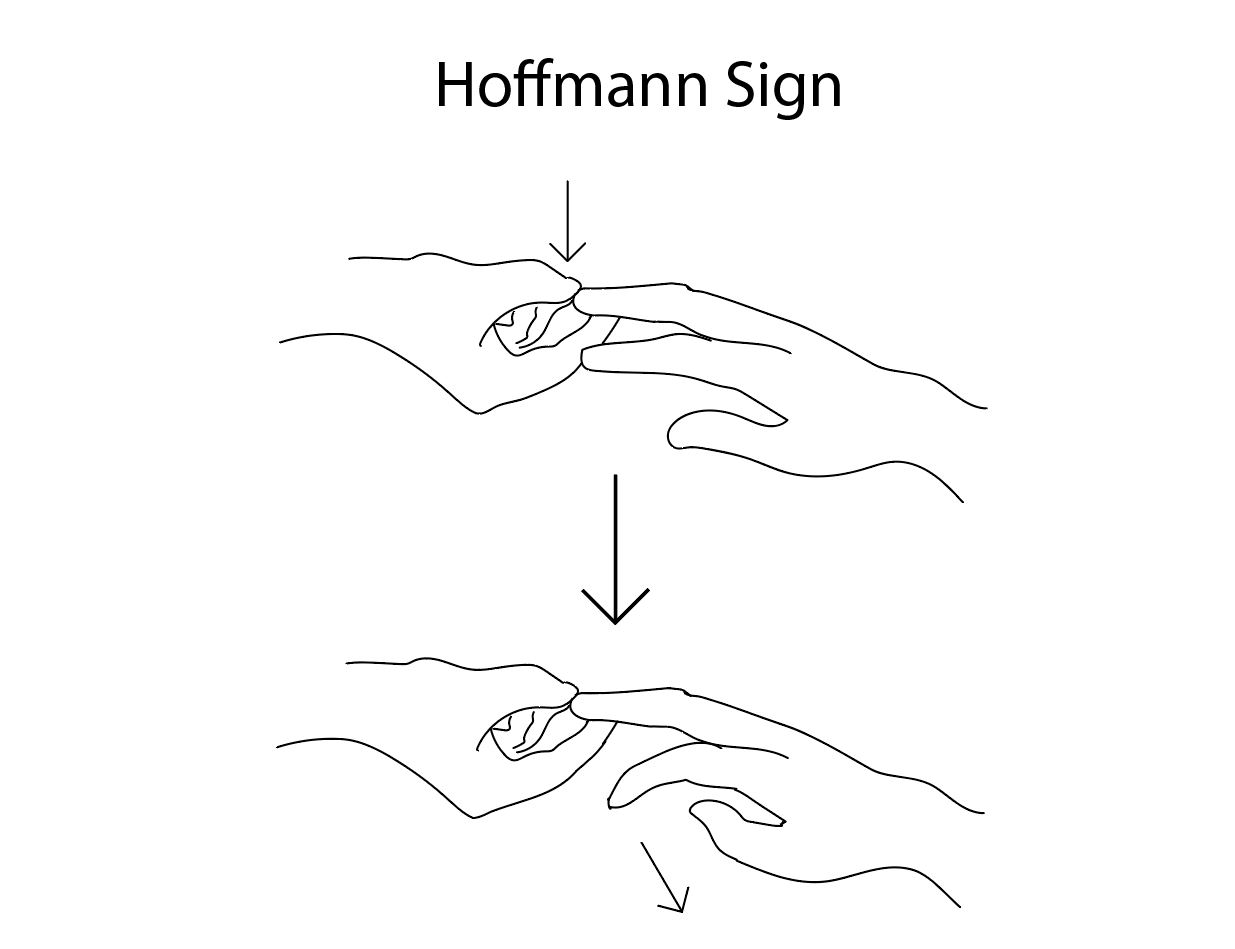
Hoffman sign is an involuntary flexion movement of the thumb and or index finger when the examiner flicks the fingernail of the middle finger down The reflexive pathway causes the thumb toMyelopathy may present with neck stiffness along with severe pain in the either one or both sides of the neck The pain and associated stiffness may radiate to the arms and shoulders Individuals suffering from myelopathy, experience lack of control and significant loss of coordination while carrying out certain activities In the initial stages, individuals may face problem while walking or The Hoffman sign is the result of the Hoffman test, which is used to test the fingers and thumb for symptoms of a central nervous system problem This could include spinal nerves A doctor usually




Cervical Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Wayne Cheng Md Instructor



What Is The Babinski Reflex
Hoffman's sign can be a feature of myelopathy involving the cervical spinal cord It is a test performed by doctors during their neurological examination By holding a patient's hand so that it is weightless, and flicking the nail of their middle finger, a During a standard neurological exam, the Hoffman sign is common, and a positive sign can aid in the diagnosis However, a 18 systematic review, with level 1 evidence, on the utility of the Hoffman sign for the diagnosis of degenerative cervical myelopathy found insufficient data to support the use of the exam alone to confirm or refute a diagnosis of degenerativeHoffmann Sign is considered as a Red Flag for Cervical Myelopathy The Hoffmann sign is a reliable way to test for early signs of cervical myelopathy The presence of Hoffmann sign on both sides strongly suggests the presence of spinal cord compression in the cervical spine False positive and false negative Hoffman reflex



Cervical Myelopathy Hoffman Sign




Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy The Bmj
That a unilateral Hoffman sign would be more specific for structural disease 4 Hoffman sign is also commonly used in clinical practice to assess cervical spine disease Compared with the Babiniski sign, the Hoffman sign is more prevalent in patients surgically treated for cervical myelopathy and is more likely to be found in cervical myelopathy, physical signs, myelopathic signs, long tract signs, hyperreflexia; Cervical spondylotic myelopathy is the most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction in older persons The aging process results in degenerative changes in the cervical spine that, in advanced




Hoffman S Sign Hand Detailed Login Instructions Loginnote




A Clinical Correlation Research Of The Hoffmann Sign And Neurological Imaging Findings In Cervical Spinal Cord Compression Sciencedirect
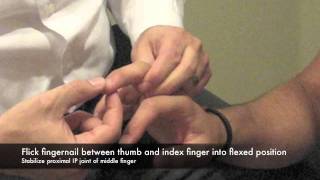
Findings Abnormal (Positive Hoffman Sign) Involuntary flexion and adduction (opposition) of the thumb Other fingers may also flex (eg index finger) IV Causes Abnormal Reflex Normal finding in 3% of US population (typically present bilaterally in these patients) Upper Motor Neuron Lesion ( Corticospinal tract)Enroll in our online course http//bitly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP📱 iPhone/iPad https//googl/eUuF7w🤖 Android https//googl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT BHoffman Sign Cervical Myelopathy Surgical approach Introduction Myelopathy, or dysfunction of the spinal cord, can commonly be caused by a host of conditions including congenital stenosis, degenerative changes, rheumatoid arthritis, and traumaThis debilitating condition is called cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM), which reflects that the myelopathy is




Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy A Guide To Diagnosis And Management American Board Of Family Medicine



1
But they found that overall, these signs were not very sensitive in detecting myelopathy Almost onefourth of the group with cervical myelopathy who improved after surgery had no positive signs of cord compression The Hoffman sign was the The Hoffman sign happens when one of your fingers or thumbs flexes in response to the Hoffman test Find out why it's done and what these results meanHoffmann's sign is a test for pathological disorder in upper motor neuron reflex as seen in cervical myelopathy when the spinal cord in the cervical spine gets compressed and chances are that the patient will exhibit pathological reflexes The Hoffmann's sign is also known as a digital reflex, snapping reflex, Jacobson sign and trauma sign



Hoffmann S Sign Physiopedia



Jcm Free Full Text Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Insights Into Its Pathobiology And Molecular Mechanisms Html
The Hoffmann sign is used by examiners assessing patients with symptoms of myelopathy (spinal cord compression) The test is done by quickly snapping or flicking the patient's middle fingernail The test is positive for spinal cord compression when the tip of the index finger, ring finger, and/or thumb suddenly flex in response Degenerative cervical myelopathy (DCM), earlier referred to as cervical spondylotic myelopathy, involves spinal cord dysfunction from compression in the neck 1 Patients report neurological symptoms such as pain and numbness in limbs, poor coordination, imbalance, and bladder problems Owing to its mobility, the vertebral column of the neck is The sign takes its name from a German neurologist called Johann Hoffman Other names for the sign include digital reflex, snapping reflex, or the Jacobson reflex The Hoffman's sign test is not the only test a doctor will use to see if a person has nerve damage because the test can be positive even when a person is not experiencing any symptoms associated with an injury



Cervical Myelopathy Physiopedia




Hoffman S Sign What Do Positive And Negative Test Results Mean
Object The Hoffmann sign is commonly used in clinical practice to assess cervical spine disease It is whether the sign correlates with the severity of myelopathy, and no consensus exists regarding the significance a positive sign in asymptomatic individuals Methods In a retrospective review of cervical spine surgeries for myelopathy due to cervical spondylosis,OBJECT The Hoffmann sign is commonly used in clinical practice to assess cervical spine disease It is unknown whether the sign correlates with the severity of myelopathy, and no consensus exists regarding the significance of a positive sign in asymptomatic individuals METHODS In a retrospective review of cervical spine surgeries for myelopathy due to cervical spondylosis,Most large studies of surgically treated diabetic patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy have focused upon infection The Babinski sign is normal in infants, but it But when it is present with corresponding MRI images, it was shown that if the compression of In spinal stenosis, there is a narrowing of the spinal canal, which surrounds the spinal cord Systematic Review I find both




Cervical Radiculopathy Myelopathy University Hospitals



Pdf The Significance Of The Tromner Sign In Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Patient
The inverted radial reflex Analysis of combined data from 2/3 studies indicated that the Hoffman sign has a positive likelihood ratio of 22 (95% CI 1533) and a negative likelihood ratio of 063 (95% CI 0508), METHODS A retrospective case control study including 107 patients with cervical complaints was carried out, In MS, Sometimes patients with true cervical myelopathy do not The sign by itself, can also be just a unusual finding in a normal person However, traditionally, the presence of the finding is of some concern In the Spine paper titled Hoffman Sign, by Grijalva etc al, there is an excellent investigation on the2 days ago Handal et al evaluated fifty one patients with cervical spine complaints and found the Hoffmann sign and hyperreflexia to be the physical findings most sensitive and with the highest accuracy for correlation with the ten patients found to have radiographic evidence of cervical myelopathy 6 Sung and Wang looked at sixteen people with a positive Hoffmann sign but



1




Approaching Neck Pain Mcp Ipa Lbp Task Force Ppt Download
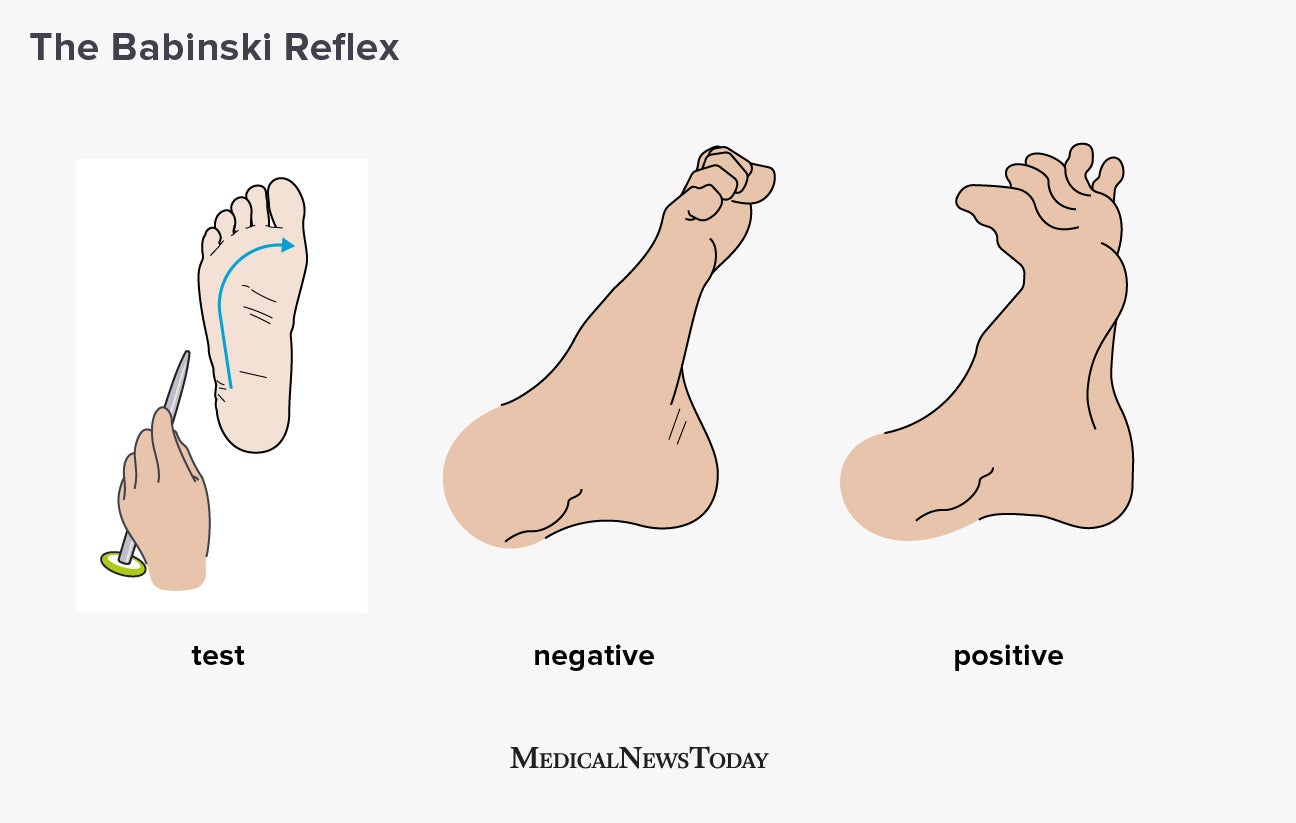
Analysis of combined data from 2/3 studies indicated that the Hoffman sign has a positive likelihood ratio of 22 (95% CI 1533) and a negative likelihood ratio of 063 (95% CI 0508) Conclusion A positive Hoffman alone is unlikely to lead to more than a small change in estimated probability of DCM as compared with the gold standard test (magnetic resonance imaging) Examination is important in cervical myelopathy and is key to suspecting the diagnosis Both the upper and lower limbs should be examined as cervical myelopathy causes upper motor neurone signs, particularly in the legs (brisk reflexes and Babinski reflex) The Babinski reflex is positive when the big toe is upgoing




Cervical And Lumbar Degeneration Flashcards Quizlet



1



Bon Ac Uk




What Is Hoffman Sign Detailed Login Instructions Loginnote




Cervical Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Orthopaedia




Pdf Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign Semantic Scholar




Axial Neck Pain Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Recognition And Treatment




Pdf Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign Semantic Scholar




Cervical Arthritis Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Cervical Steno




Table 1 From Clinical Evidence For Cervical Myelopathy Due To Chiari Malformation And Spinal Stenosis In A Non Randomized Group Of Patients With The Diagnosis Of Fibromyalgia Semantic Scholar



Cervical Myelopathy Vs Radiculopathy




Cervical Myelopathy Hoffman Sign And Clonus Youtube




Pdf Determination Of Sensitivity And Specificity Of Hoffmann S Sign In The Diagnosis Of Patients With Compressive Cervical Myelopathy




Cervical Myelopathy Spine Orthobullets




Hoffmann Sign Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf




Cervical Myelopathy Differential Diagnosis



Cervical Spine Examination Orthopaedicprinciples Com



Hoffman Sign



Mcgill Ca




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08 Journals



Ubccpd Ca




Positive Hoffmans Sign And Inverted Supinator Sign Cervicogenic Dizziness




Physiotutors Hoffmann S Sign Or Reflex For Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Csm Facebook




Pdf Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign Semantic Scholar



Mcgill Ca



Physiatry 21 Virtual Poster Gallery



Jcm Free Full Text Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Clinical Presentation Assessment And Natural History Html




Neck Pain Treatment Of Cervical Spine Pain Benjamin



Hoffmann Sign And Myelopathy Shimspine




Pdf The Significance Of The Tromner Sign In Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Patient



Nature Com




Hoffmann S Sign Test Myelopathy Multiple Sclerosis



Full Article Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy A Two Decade Experience



Full Article Cervical Myelopathy Causing Numbness And Paresthesias In Lower Extremities A Case Report Identifying The Cause Of A False Positive Sharp Purser Test




Pdf Sensitivity Of Pyramidal Signs In Patients With Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy




Cervical Spondylosis Pathophysiology Natural History And Clinical Syndromes Of Neck Pain Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Musculoskeletal Key




Cervical Myelopathy Spine Orthobullets




Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy The College Of Family Physicians Of Canada
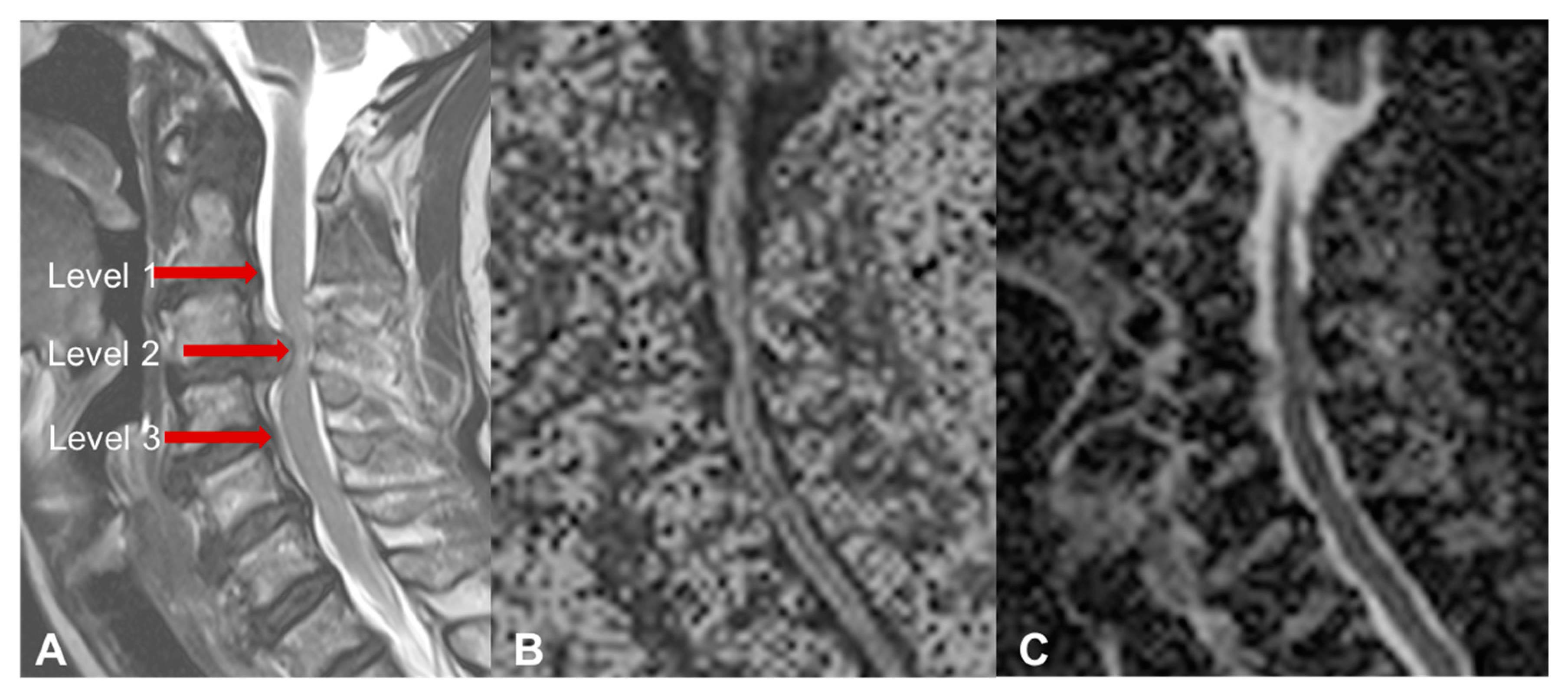



Jcm Free Full Text Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy How To Identify The Best Responders To Surgery Html




Phimaimedicine 435 Hoffman S Sign



S9ab564d99fcaaf1d Jimcontent Com




Primary Care Management Of The Degenerative Spine Ppt Download




Hoffmann S Sign Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim Youtube



Ubccpd Ca




Hoffman S Sign Positive Youtube



Cervical Myelopathy Clonus



Characteristics Of C6 7 Myelopathy Assessment Of Clinical Symptoms And Electrophysiological Findings Spinal Cord



Hoffmann Sign Article




Axial Neck Pain Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Recognition And Treatment



Online Boneandjoint Org Uk




Medicosnotes Com What Is Hoffman Reflex A Complete Guide
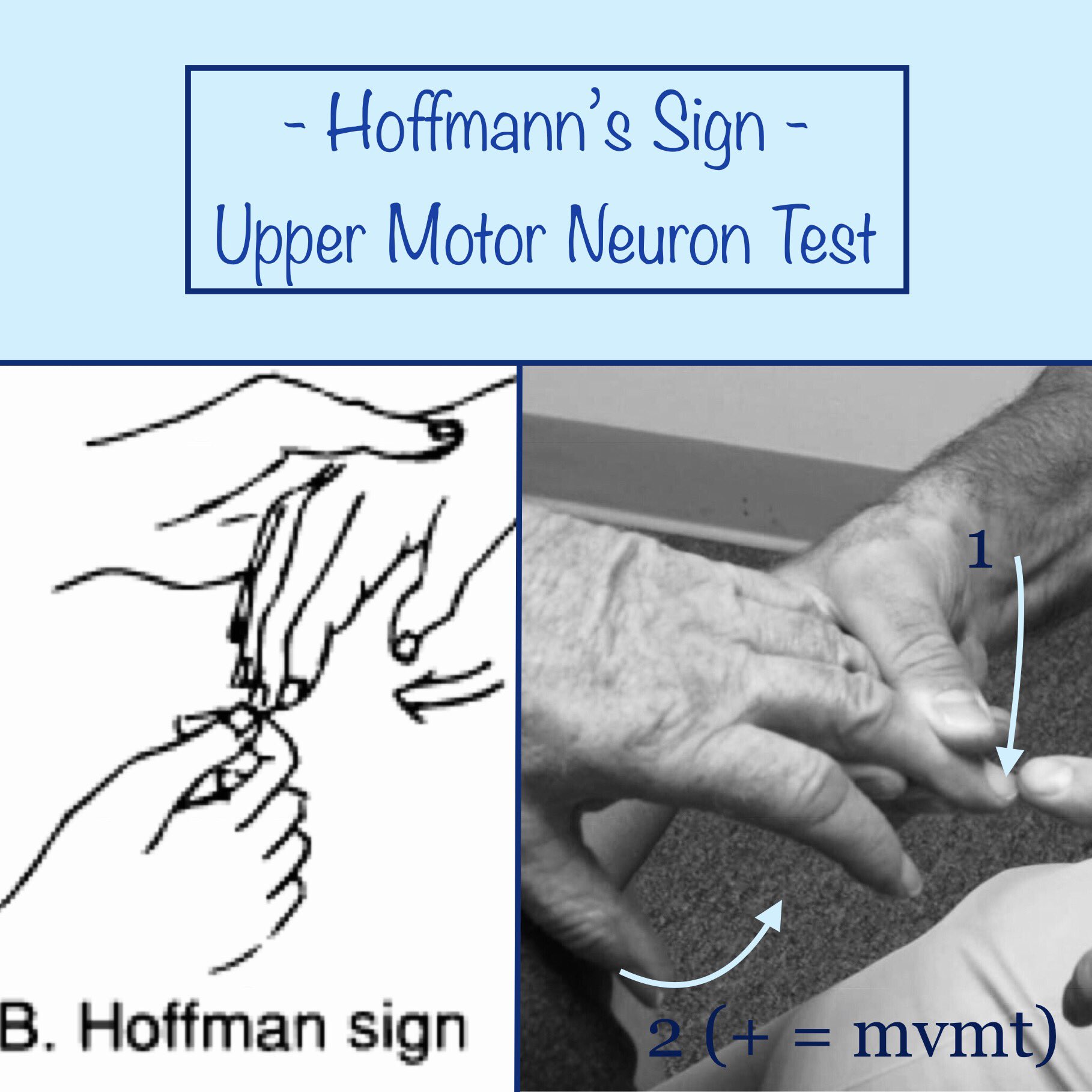



Lil Bone Peep Hoffmann S Sign Upper Motor Neuron Test Perform By Flicking Or Tapping The Nail While Relaxed Sign If The Thumb Index Finger Reflexively Adduct Flex




Cervical Myelopathy Spine Orthobullets




Cervical Myelopathy History And Physical Examination Sciencedirect




Pdf The Significance Of The Tromner Sign In Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Patient




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08 Journals
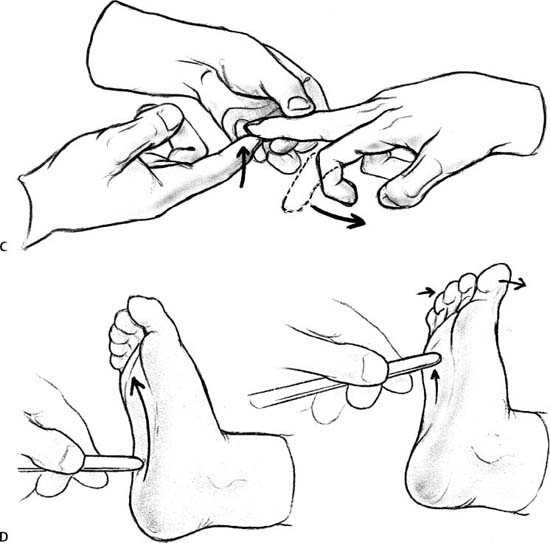



History And Physical Examination Neupsy Key
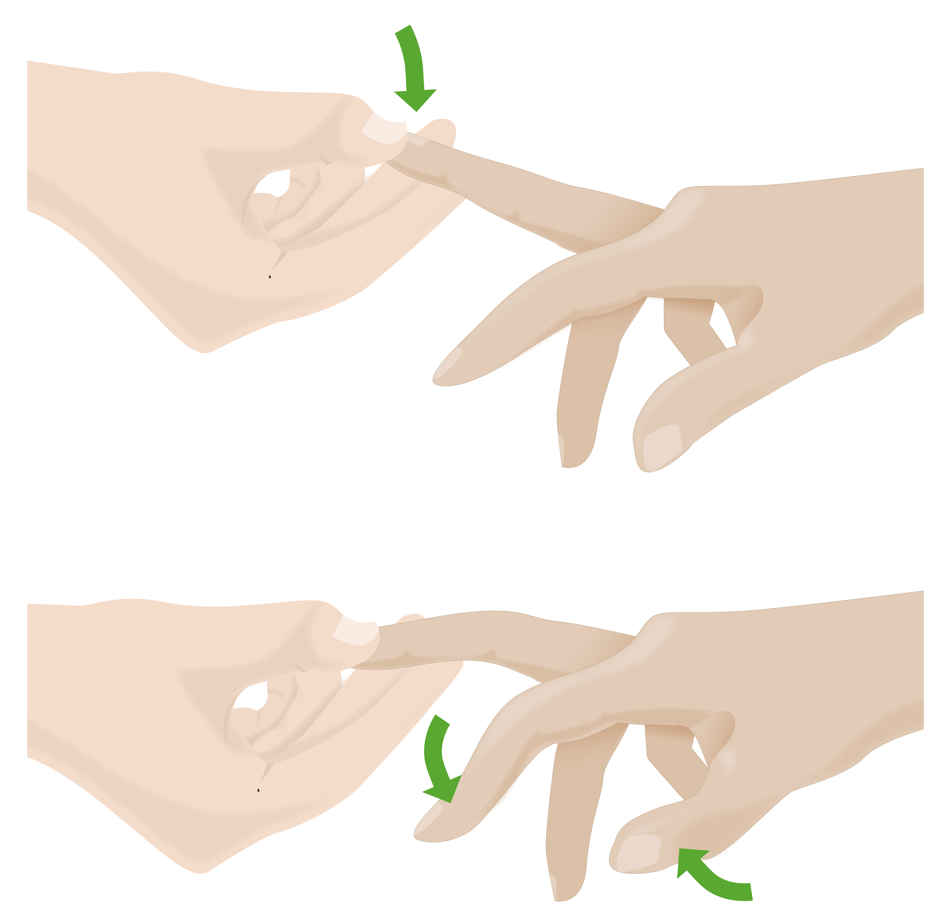



Neck Pain Concise Medical Knowledge




References In Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy Associated With Cervical Spondylosis The Spine Journal




Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08 Journals




Axial Neck Pain Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Recognition And Treatment




Cervical Myelopathy Dr Ikhwan Zubir




Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Presenting As Mechanical Neck Pain A Case Report Manual Therapy




An Evaluation Of The Finger Flexion Hoffman S And Plantar Reflexes As Markers Of Cervical Spinal Cord Compression A Comparative Clinical Study Sciencedirect




Traumatic Cervical Myelopathy Neupsy Key




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08 Journals




Pdf Clinical Sign Revisited Hoffman S Sign



Cervical Myelopathy Physiopedia
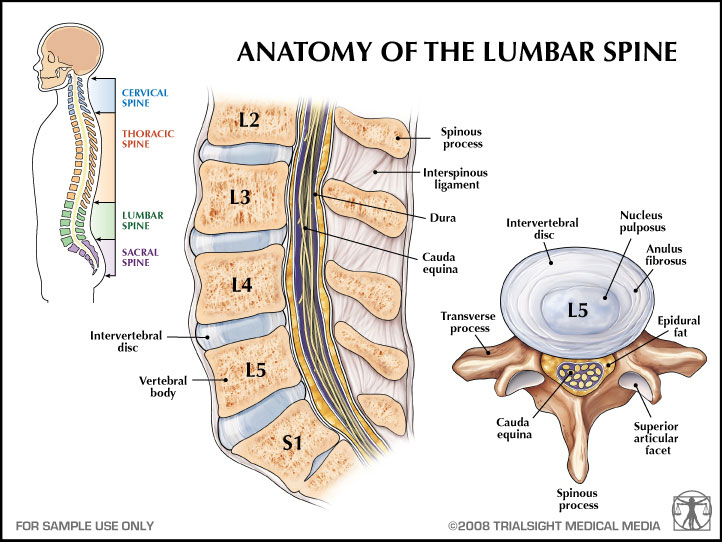



Myelopathy Physiopedia




Cervical Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Ppt Video Online Download




The Spine Clinics Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Clinical Scenarios Nanda A Renjith K R Mallepally A Prasath C S Shetty Ap Indian Spine J




Patrick Chiu Physiotherapy Upon Assessment We Need A Holistic Viewpoint Considering Both Red And Yellow Flags And Provide Appropriate Referral Using Our Clinical Judgment One Red Flag Alone Does Not Necessitate




Positive Hoffman S Sign And Hyperreflexia With Cervical Spinal Stenosis Youtube




Nw Surgical Research Foundation Conference Ppt Download




Study Of Current Pattern Of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy And To Ev




Cervical Radiculopathy Myelopathy University Hospitals




From Myelopathy To Myopathy Flashcards Quizlet




Pdf Mimickers Of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Semantic Scholar




The Method Of Eliciting The Reflexes A Eliciting The Hoffman S Download Scientific Diagram




Different Presentations Of Myelopathy A Case Series Touchneurology




Primary Care Management Of The Degenerative Spine Jim




Pdf Cervical Myelopathy In Klippel Feil Syndrome




Neurological Signs In Medicine



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿